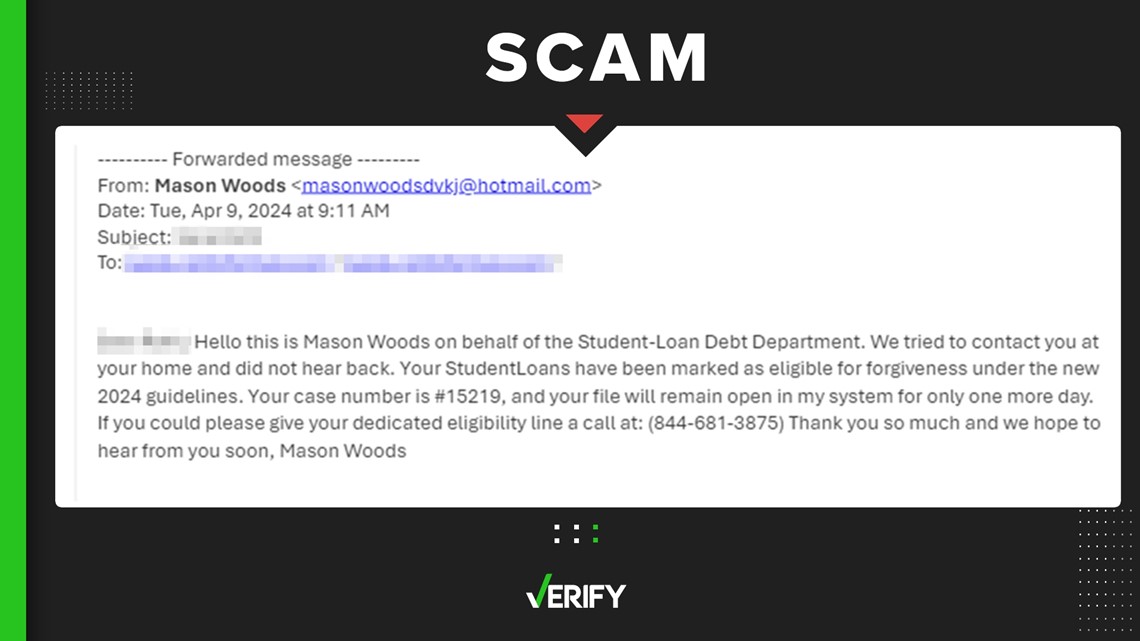
Q2 2024 of the Email Threat Trends Report*, highlights the ingenuity of cyber criminals in using AI to evade detection and maliciously scam individuals and enterprises. VIPRE processed 1.8 billion emails globally, detecting 226.45 million spam emails and 16.91 million malicious URLs to identify the email threat trends that impact enterprises the most.
The high stakes of Business Email Compromise (BEC)
BEC remains a major scourge. Nearly half (49%) of all detected spam emails are attributed to BEC scams, with the CEO, followed by HR and IT, being the most common targets. It takes on a more sinister complexion when a full 40% of the BEC emails uncovered were AI-generated, and in some instances, AI likely created the entire message.
Double the malicious attachments
Q2 2024 saw twice as many evasive malicious attachments compared to the previous year, underlining the sophistication of modern email exploits. Entities without measures to detect these advanced threats could find themselves in hot water, facing double the risk compared to 12 months ago.
74% increase in malicious links
The research identified 16.91 million malicious URLs, a 74% rise from the previous year. This surge highlights the growing use of advanced evasion techniques by attackers.
Emerging trends in phishing and malspam
Phishing remains a dominant threat with attackers favouring URL redirection and cloud-hosting services. Cloudflare Turnstile was the most commonly used technique (51%) in phishing emails. Cloudflare Turnstile is a free service designed to protect websites from malicious traffic and functions as an advanced CAPTCHA alternative.
A significant shift in malspam tactics is observed. 86% of malspam emails used malicious links and only 14% contained attachments – a reverse of the Q1 2024 trend, where 78% of malspam emails contained malicious attachments, while only 22% used malicious links. This swing may be due to the increasing difficulty in detecting malicious links leading to seemingly legitimate websites that harbor infected links.
Sector-specific targeting
Threat actors increasingly targeted the manufacturing sector with 25% of email attacks, followed by retail (which was absent from 2023’s targets) at 20% and real estate at 11%. Attackers appear to be focusing on industries perceived as lacking advanced cybersecurity measures. In 2023, finance led the way with 25% of email attacks, and manufacturing surged to 43% in Q1 2024, a top position the sector continues to hold.
Regional spam sources
The US continues to be the top contender when it comes to sending and receiving spam (receiving nearly half of all phishing emails), most likely thanks to its vast data center infrastructure. Consistent with last quarter, the UK was the second-largest source of spam, followed by Canada, Sweden, and Iceland; three countries that failed to make the list either last quarter or this time last year.
“As AI technology advances, the potential for BEC attacks grows exponentially. Malefactors are now leveraging sophisticated AI algorithms to craft compelling phishing emails, mimicking the tone and style of legitimate communications,” Usman Choudhary, Chief Product and Technology Officer, VIPRE Security Group, says. “The next wave of BEC attacks could see attackers using AI to dynamically analyse and exploit real-time information, creating tailored and contextually accurate scams nearly indistinguishable from genuine correspondence. Enterprises must stay ahead by adopting robust AI-driven defenses and continuously educating their workforce on emerging threats.”
*Report from VIPRE Security Group
www.VIPRE.com